About Materials Engineering
Materials engineers design, produce and evaluate materials and their use. They bring valuable expertise in materials to just about every industry, often working closely with other engineers, to make a real difference to our world.
The Materials Engineering program at UBC provides the knowledge and skills you need to pursue your career goals. Students enter the program after the 1st year of Engineering or equivalent study. It takes 3 further years to complete and achieve a Bachelor of Applied Science, 4 years with the Co-op option.
What is Materials Engineering?
Materials engineering is all around us. From buildings to transportation to the electronic devices we use every day, the materials involved have been designed or chosen carefully for the task.
Materials have an important role in every field of engineering. The materials we use and how we make them can determine the function, feasibility, cost, environmental impact and many other aspects of things we create.
Take your computer or cell phone as an example and ask yourself, “Why is it made out of these materials?” or, “Why is it designed in this particular way?” or even, “Would it be possible to make it if it was not made from these materials?” To answer such questions, we must delve into the world of materials engineering.

What do materials engineers do?
Materials engineers are experts on materials – how they are made, how and why materials are useful, and how materials can be made better. Materials engineers are concerned with every stage of a material’s lifecycle from mining to recycling. They design new materials, devise processes for making materials and disposing of them, they select the best material for a particular job, monitor its performance and figure out why a material failed.
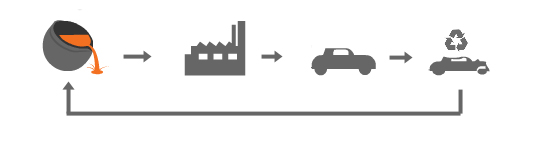
To do this, materials engineers need to understand the scientific principles that underlie the relationship between how a material performs and its structure/composition. They bring expertise on the properties of materials – chemical, physical and mechanical.
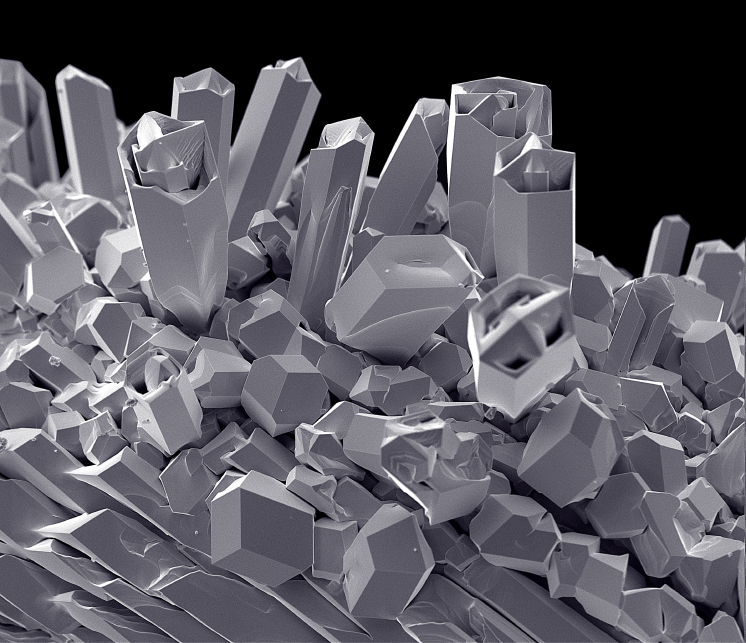
From the electron microscope: Understanding the structure of a material provides insight into how it can be used and why it could fail.
Materials engineers take science innovations and use them in real world applications that exploit their desirable properties – and so they work closely with many other disciplines in science and engineering.

Composite materials offer a weight advantage over metals for many applications but pose significant challenges that must be solved to fully realize the benefits.